2 min read
Prototyping Model
- Sanjay Thakur
- Jun 28, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Aug 9, 2022

The prototyping model is applied when there is an absence of detailed information regarding input and output requirements in the software. The prototyping model was developed on the assumption that it is often difficult to know all the requirements at the beginning of a project. It is usually used when a system does not exist or in the case of a large and complex system where there is no manual process to determine the requirements.
This model increases the flexibility of the development process by allowing the user to interact and experiment with a working representation of the product known as prototype. Generally, prototyping can be prepared by the approaches listed below.
By creating major user interfaces without any substantive coding in the background to give the users a feel of what the system will look like.
By abbreviating a version of the system that will perform limited subsets of functions.
By using system components to demonstrate functions that will be included in the developed system.
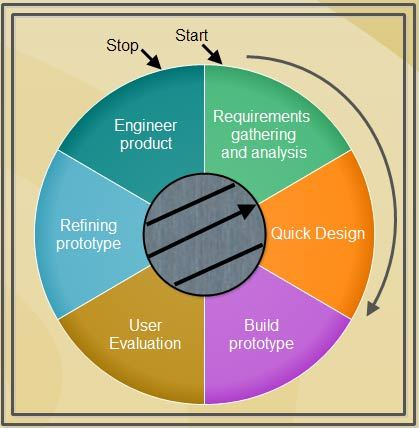
The Prototyping Model
Requirements Gathering and Analysis: A prototyping model begins with requirements analysis, and the requirements of the system are defined in detail. The user is interviewed to know the requirements of the system.
Quick Design: When requirements are known, a preliminary design or quick design for the system is created. It is not a detailed design, however, and includes the important aspects of the system, which gives an idea of the system to the user. A quick design helps in developing the prototype.
Build Prototype: Information gathered from quick design is modified to form a prototype. The prototype of the required system is developed from quick design. It represents a 'rough' design of the required system.
Assessment of User Evaluation: Next, the proposed system is presented to the user for consideration as a part of the development process. Comments and suggestions are collected from the users and are provided to the developer.
Prototype Refinement: Once the user evaluates the prototype, it is refined according to the requirements. The developer revises the prototype to make it more effective and efficient according to user requirements.
Engineer Product: Once the requirements are completely known, the user accepts the final prototype. The final system is thoroughly evaluated and tested followed by routine maintenance on a continuing basis to prevent large-scale failures and minimize downtime.



Comments