2 min read
Quantum Computing
- Punish Rathore

- Jun 29, 2022
- 1 min read
Updated: Aug 9, 2022
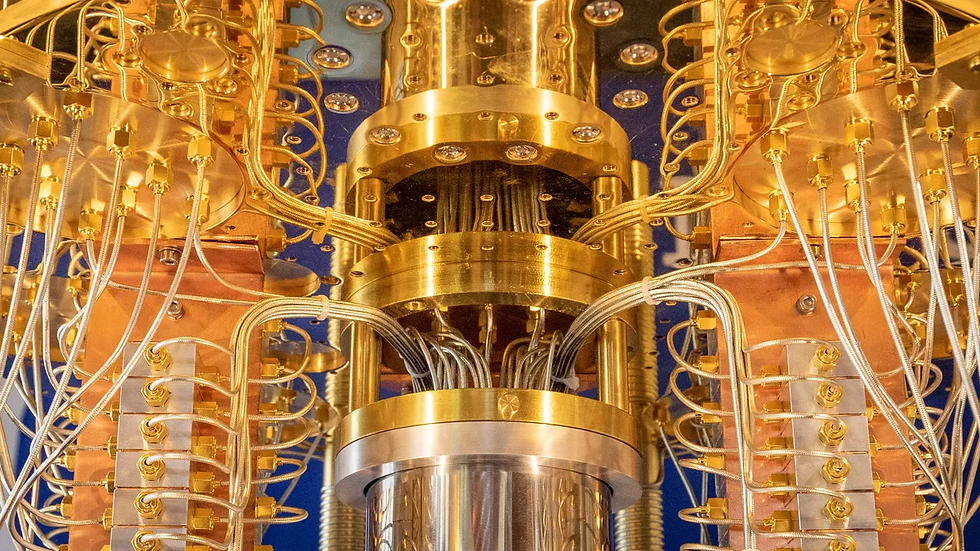
Quantum computing is a future technology in which quantum physics is used to calculate problems that are very complex for classical or conventional computers. Quantum computers will allow for data storage and processing in ways we cannot even comprehend today. They also offer more complex calculations than traditional computers and can quickly solve problems that would take years to solve on a conventional computer.
Do quantum computers exist now? In September of 2020, IBM revealed they developed one of the largest existing quantum computers in the world, consisting of 65 qubits. The company has already identified several areas in which the complexity of quantum computing capabilities may be applied.
In 2019, Google announced that its Sycamore quantum computer had completed a task in 200 seconds that would take a conventional computer 10,000 years. (Other researchers would later describe a way to greatly speed up the ordinary computer’s calculation.)
What's in the Future
Quantum computing can be a game-changer in fields such as cryptography, chemistry, material science, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals once the technology is more mature.
Quantum computing has a dynamic nature, acting as a useful solution for complex mathematical models, such as:
Encryption methods have been designed to take centuries to solve even for supercomputers. However, these problems could possibly be solved within minutes with quantum computing.
Even though the modeling of a molecule does not seem to happen in the near future with classical computing, quantum computing can make it possible by solving equations that impede advances in extracting an exact model of molecules. This development has the potential to transform biology, chemistry, and material science.



Comments